OPTICS | Part -1 |
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
STUDY NOTES
For Part - 2 | Optics
- Light is an electromagnetic wave.
- it doesn’t require any material medium for travel.
- It possess both particle as well as wave
- Light takes straight path for their travel.
- The straight line path of light is termed as Light Ray.
- Group of more than two light rays are termed as beam of light.
- It also causes shadow formation.
- The speed of light is 3,00,000 kilometres per second.
- When any light ray incidents on any surface than there three possible phenomenon are possible.
- In the diagram shown below the image of glass is due to reflection and the spoon is bends slightly due to reflection of light
- Reflection of light :- In this case light ray reflects back into the same medium after reflection by reflecting surface.
- Refraction of light :- in this case light ray cross the surface and we can see across that surface.
- Absorbtion of light :- in this case light energy is absorbed by surface.
Reflection of light:
- When light gets incident on any reflecting surface and bounces back to the same medium then this phenomenon of light is called reflection of light.
- There two types of reflection on the basis of nature of surface.
- Regular refelection
- Diffused reflection
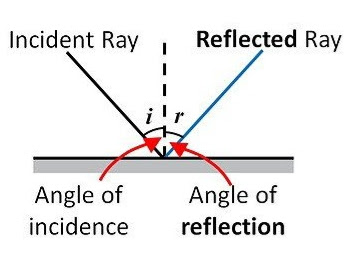
Laws of reflection of light: There are two laws of reflection. These laws are applicable for all types of reflecting surfaces. They are:
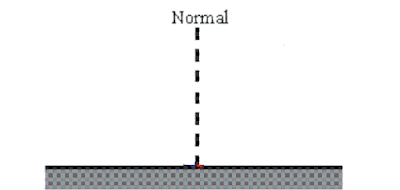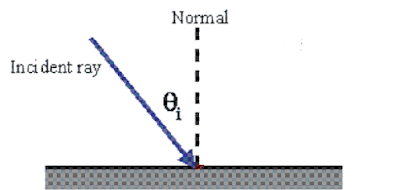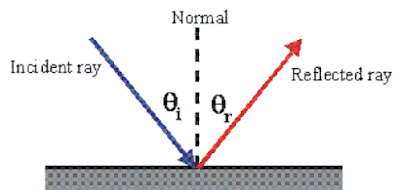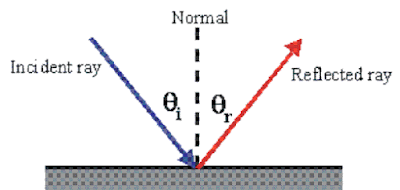
- The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection. i.e. ∠i = ∠r
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal to the plane at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
MIRRORS :-
Mirrors are 100% refelctors.
It is used to reflectes light rays into the same medium.
Silver is used as reflector in mirror.
Types of mirrors:
There are two types of mirrors.
- plane mirrors
- spherical mirrors.
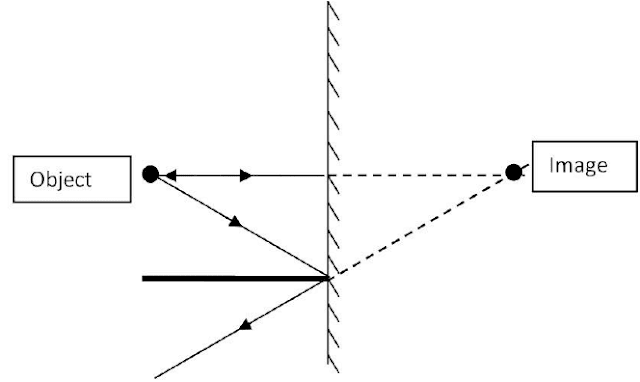
- Plane mirror :- To form a plane mirror one side of a plane glass surface is polished by reflecting material (silver).
- Image is virtual and erect.
- The size of image is same as size of object.
- The distance of image from mirror is same as the distance of object from mirror.
- A plane mirror forms laterally inverted
Laterally inverted image of F is shown in FIGURE above.
- Magnifcation of plane mirror is +1. Where positive sign shows that image is Virtual and 1 shows that size of image is same as size of object.
Lateral inversion:
When left side of the object appears right in the image and vice versa is said to be lateral inversion.
- There are many uses lateral inversion. We see on Ambulance written laterally inverted and we see it actual in our side mirror.
Laterally inverted image of AMBULANCE
Working of periscope
Uses of plane Mirror :-
- Plane mirror can be used to see ourself at home.
Plane mirror can be used as periscope in submarine.
Working of periscope
- Spherical mirrors:
- Spherical mirror is a part of a sphere.
- To get a spherical mirrors one side of a spherical surface is polished by reflecting material.
- Their are two sides in spherical surface.
- Inner side
- Outer side
Types of spherical mirrors:
There are two types of spherical mirrors:
Concave mirror:
- A spherical mirror whose outer side is polished by reflecting material is said to be concave mirror.
- It is also called converging mirror as it converges parallel beam of light falling on it.
- Concave mirror can form both real and virtual image.
- Focal length for cancave mirror is always negative.
Uses of concave mirror :-
- In Search light and touch to produce parallel beam of light.
- It can be used by dentist to see larger image of teeth.
- It can be used in headlights of vehicle.
- It can be used in shaving mirror.
Convex mirror
- A spherical mirror whose inner side is polished by reflecting material is said to be convex mirror.
- It is also called diverging mirror as it diverges parallel beam of light falling on it.
- Canvex mirror always forms virtual image.
- The size of image formed by convex mirror is always smaller than size of object.
- Magnifcation of convex mirror is m < +1.
- Focal length for convex mirror is always positive.
- Convex mirror has larger field view area.
NOTE :- If we want to form a real image from convex mirror and we have to replace real object by virtual object.
Uses of Convex mirror :-
Some definations related to spherical mirrors:
Uses of Convex mirror :-
- It can be used as rear view mirror in vehicle to see vehicles behind our car. Because it has larger field view area.
- It can be used as side view mirror in vehicles
- It can be used in shop and shopping malls to watch their customers.
- At danger traffic turns it is used to see the opposite comers.
Some definations related to spherical mirrors:
- Principal axis: Pole and center of curvature is joined by a line called principal axis.
- Pole: The center of the mirror is pole. We denote it by ‘P’.
- Aperture: The effective length of the mirror is aperture.
- Center of curvature: The center of the sphere which mirror is a part is center of curvature. It is denoted by ‘C’.
- Radius of curvature: The radius of the sphere which mirror is a part is radius of curvature.
- Focus: When parallel light beam is incident on the spherical mirror, then after reflection, the point at which they meet or appears to meet is said to be focus of that mirror.
- Focal length: The length of the line joining pole and focus of the spherical mirror is its focal length. It is denoted by the symbol ‘f’.
Ray diagram:
There are certain rules we should follow to make ray diagrams which will further used in understanding light reflection and refraction.
-
A beam of parallel rays incident on spherical mirror after reflection passes through focus. In case of concave mirror the reflected ray converges to focus but in case of convex mirror the ray appears to diverge from focus

- The incident ray when passes through focus after reflection it passes parallel to the principal axis.
- A ray incident on the spherical mirror passing through center of curvature returns back on same path.
- A ray incident to the pole of the mirror after reflection makes equal angle with the principal axis.
Image formation by concave mirror
When object is placed at infinity:-
Properties of image :-
-
Image is point sized.
-
Image is real.
-
Image formed at Focus.
When object is placed beyond C:-
Properties of image:-
When obejct is placed at C :-
- Image is real and inverted.
- Image formed between F and C.
- The size of image is smaller than object.
Properties of image:-
- Image is real and inverted.
- Size of image is same as size of object.
- Image is formed at C.
- Image is real and inverted.
- Image formed beyond C.
- Size of image is larger than size of object.
When object is placed at F:-
- Image is real and inverted.
- Image formed at infinity.
- Size of image is very large as compared to object.
When object is placed between F and P:-
- Image is virtual and erect.
- Size of image is larger than size of object.
- Image formed behind the mirror.
Images formed by convex mirror:
When object is placed at infinity:-
Properties of image:-
- Image is virtual and point sized
- Image formed at Focus.
When object is placed beyond P :-
Properties of image:-
- Image is virtual and erect.
- Image formed between P and F.
- Size of image is smaller as compared to object.
Sign convention used in spherical mirror:
These observable conventions will help you in solving numerical related to light reflection and refraction.
- Object is always placed to the left of mirror.
- All distance are measured from pole of the mirror.
- Distances which are measured in the direction of incident ray are positive.
- Distances which are measured in the opposite direction of incident ray are n
- All distances measured above the principal axis along y-axis are positive.
- Distances measured below the principal axis along negative y-axis are negative.
Note: Object distance (U) is always negative, focal length of concave mirror is negative where convex mirror is positive.
Mirror formula:
Mirror formula is expressed as.
Where:-
u = distance of object from pole of mirror
v = distance of image from pole of mirror
f = focal length of mirror
Magnification formula:
Magnification is the ratio of height of image to that of the object. It will take each case of light reflection and refraction either in mirror or lens
magnification can be expressed as
Where :-
hi = height of image
ho = height of object
di = distance of image from mirror
do = distance of object from mirror
Rules based on magnification:
- If m is negative then image is real but when it is positive then image is virtual.
- If hi = ho then m = 1, i.e. image is equal to the object, if hi > ho then m >1 image is enlarged also if hi < ho then m<1 image is diminished.
- Magnification of plane mirror is always +1.
- If m is +ve and less than 1 then it is convex mirror.
- If m is +ve and more than 1 also when m<1 then it is concave mirror
Light - Reflection| Class 10th Physics | CBSE | STUDY NOTES
 Reviewed by Er. Ashish kumar wadia
on
September 21, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Er. Ashish kumar wadia
on
September 21, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Er. Ashish kumar wadia
on
September 21, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Er. Ashish kumar wadia
on
September 21, 2019
Rating:







































No comments: